In patients with HER2+ metastatic breast cancer
Brain metastases CAN develop quickly and can significantly reduce overall survival 1- 3

More than half of patients with HER2+ MBC who develop brain metastases may do so at or before the second line of therapy1*

Median time to brain metastases after initial MBC diagnosis is approximately 1 year 2†
The presence of CNS metastases either at or after MBC diagnosis significantly reduces OS and PFS3
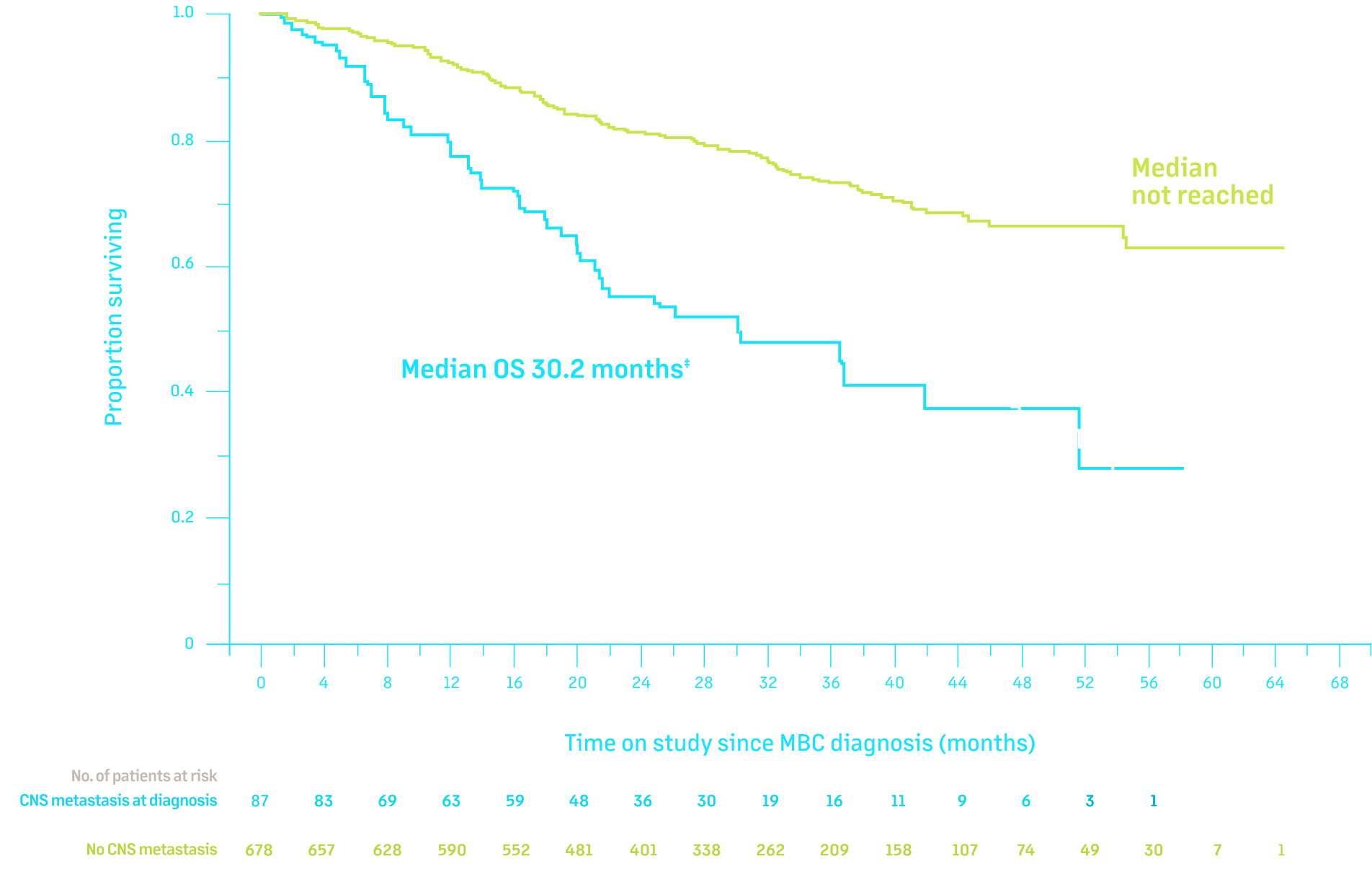
Overall survival of patients with HER2+ MBC by presence of CNS metastases3
- No CNS metastasis (n=678)
- CNS metastasis after MBC diagnosis (n=212)
- CNS metastasis at MBC diagnosis (n=87)
- No CNS metastasis (n=678)
- CNS metastasis after MBC diagnosis (n=212)
- CNS metastasis at MBC diagnosis (n=87)
Adapted from Clinical Cancer Research, 2019, Volume 25, Issue 8, 2433-2441, Hurvitz, Central Nervous System Metastasis in Patients with HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer: Patient Characteristics, Treatment, and Survival from SystHERs, with permission from AACR.
Data from the SystHERs study, a real-world analysis of 977 patients with HER2+ MBC.3
Patients with CNS metastasis also progress more quickly than those without, requiring a faster transition to the next line of therapy3
- Median PFS in patients with CNS metastases at MBC diagnosis: 9.2 months; HR = 2.49 (95% CI: 1.93-3.20); P <0.0001
- Median PFS in patients with CNS metastases after MBC diagnosis: 9.9 months; HR = 2.52 (95% CI: 2.13-2.99); P <0.0001
- Median PFS in patients with no CNS metastases: 19.1 months
*Based on a retrospective review of electronic medical records from 86 of 165 patients with HER2+ MBC with brain metastases.1
†In 226 patients with HER2+ MBC who developed initial brain metastases after MBC diagnosis.2
‡Median OS in patients with CNS metastasis at diagnosis vs no CNS metastasis at any time: 30.2 months vs not reached; HR = 2.86 (95% CI: 2.05-4.00); P <0.0001.3
§Median OS in patients with CNS metastasis after diagnosis vs no CNS metastasis at any time: 38.3 months vs not reached; HR = 1.94 (95% CI: 1.52-2.49); P <0.0001.3
THE EFFECTS OF BRAIN METASTASES ARE WIDE-RANGING AND CAN BE BOTH PHYSICALLY AND EMOTIONALLY DEVASTATING4,5

seizures

headache

dizziness

ataxia

nausea/
vomiting

visual
impairment

altered mental status
Altered mental status includes manifestations of brain dysfunction such as impaired cognition, inattention, disorientation, altered behavior, and drowsiness6
Patients with brain metastases at diagnosis may experience significant reductions in quality of life3,7
Patients with brain metastases had a significant 9-point reduction in the FACT-B (P = 0.002), exceeding the threshold for minimal important difference||
103.5
in patients without brain metastases at diagnosis
(n = 714)
VS
94.5
in patients with brain metastases at diagnosis
(n = 62)

||The FACT-B is a sum of 5 subscales (physical, functional, emotional, social, and breast cancer well-being), with a total score of 0-148.3


 are US registered trademarks of Seagen Inc.
are US registered trademarks of Seagen Inc.